VQE & NISQ
A brief overview of VQE
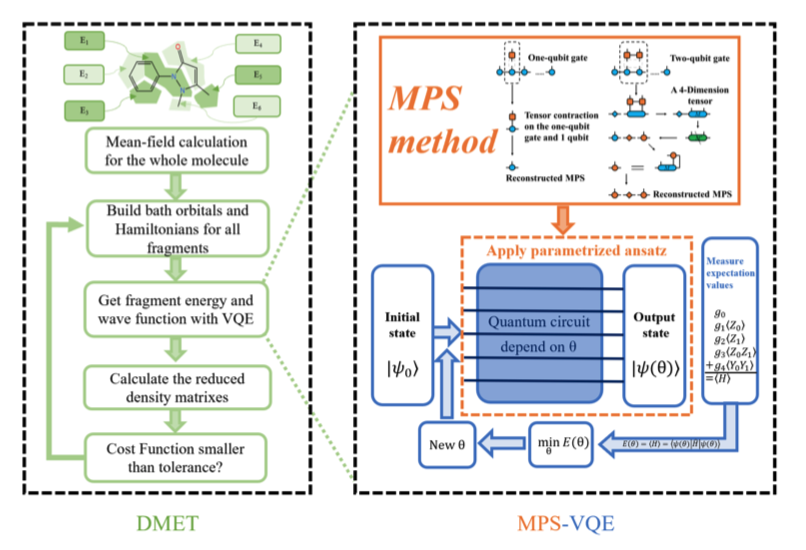
The Variational Quantum Eigensolver (VQE) is a flagship algorithm for quantum chemistry using near-term quantum computers. It is an application of the Ritz variational principle, where a quantum computer is trained to prepare the ground state of a given molecule.
The inputs to the VQE algorithm are a molecular Hamiltonian and a parametrized circuit preparing the quantum state of the molecule. Within VQE, the cost function is defined as the expectation value of the Hamiltonian computed in the trial state. The ground state of the target Hamiltonian is obtained by performing an iterative minimization of the cost function. The optimization is carried out by a classical optimizer which leverages a quantum computer to evaluate the cost function and calculate its gradient at each optimization step.
A brief overview of NISQ
Existing quantum devices contain on the or- der of 100 phyisical qubits. They are sometimes denoted as “ Noisy Intermediate-Scale Quantum (NISQ)” devices, meaning their qubits and quantum operations are not QEC(quantum error correction) and, therefore, imperfect. One of the goals in the NISQ era is to extract the maximum quantum computational power from current devices while developing techniques that may also be suited for the long-term goal of the fault-tolerant quantum computation.
